A light-emitting diode is a two-leaded semiconductor light source
An LED is a special type of diode that has the same electrical characteristics as a N junction diode, which allows the current to move through the leads and prevents the current from moving in the opposite direction. The LED occupies an area of less than 1 m㎡.

What is a light-emitting diode?
LED is a p-n junction diode whose principle is electric brightness, a material called electric brightness, which is used to convert electrical energy into light energy and later helps in the propagation of light energy, when light is emitted in a front bias, it is called a light-emitting diode.
The structure of a light-emitting diode
The materials used in LEDs are usually gallium arsenide (GAS), gallium phosphide (GAP), or gallium arsenide phosphide (GASP), any of which can be used in the construction of LEDs, but the color of the light will change with the material.
In the table below, you can see the names of the materials, as well as the corresponding colors of the light they emit:
building material
|
color
|
Forward voltage (in volts)
|
GaP
|
Green/Red
|
2.2
|
GaAsP
|
Yellow
|
2.2
|
GaAsP
|
Red
|
1.8
|
GaN
|
white
|
4.1
|
GaN
|
blue
|
5.0
|
AllnGaP
|
amber
|
2.1
|
AllnGaP
|
Yellow
|
2.1
|
How do light-emitting diodes work?
LED is nothing but a form of light-emitting diode, which we call a diode, when the diode is on the positive bias side, the electrons move quickly at the hole junction and keep connecting, so it makes the whole atom more stable and bursts a little bit of energy in the form of a small packet or photon.
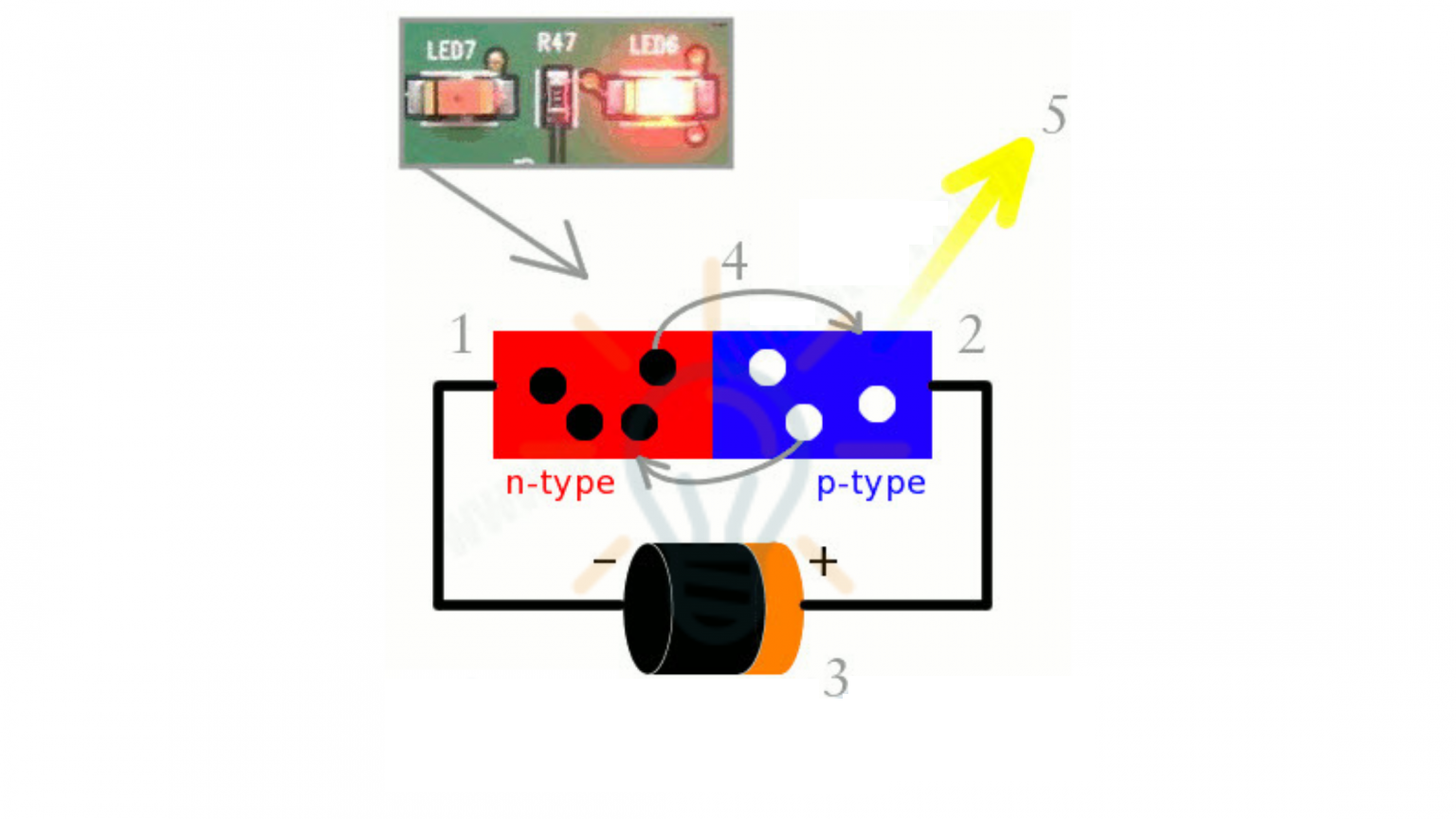
How LEDs work
As you can see from the diagram, N-type silicon is red and contains electrons, P-type silicon is blue and has holes, and the power supply of the p-n junction biases the diode forward and pushes the electrons from the n-type to the p-type. Push the hole in the opposite direction. The electrons and holes are connected at the junction, the photons are closed, and the electrons and holes are re-established.
The working principle of LEDs is based on the quantum principle. According to quantum theory, electrons move from a higher energy level to a lower energy level, and when energy is released from a photon, the distance between the two energy levels photon energy is the same. If the PN junction diode is in forward bias and current flows through the diode, the current flow in the semiconductor is due to the flow of electrons in the direction of the two currents and the current direction opposite to each other.
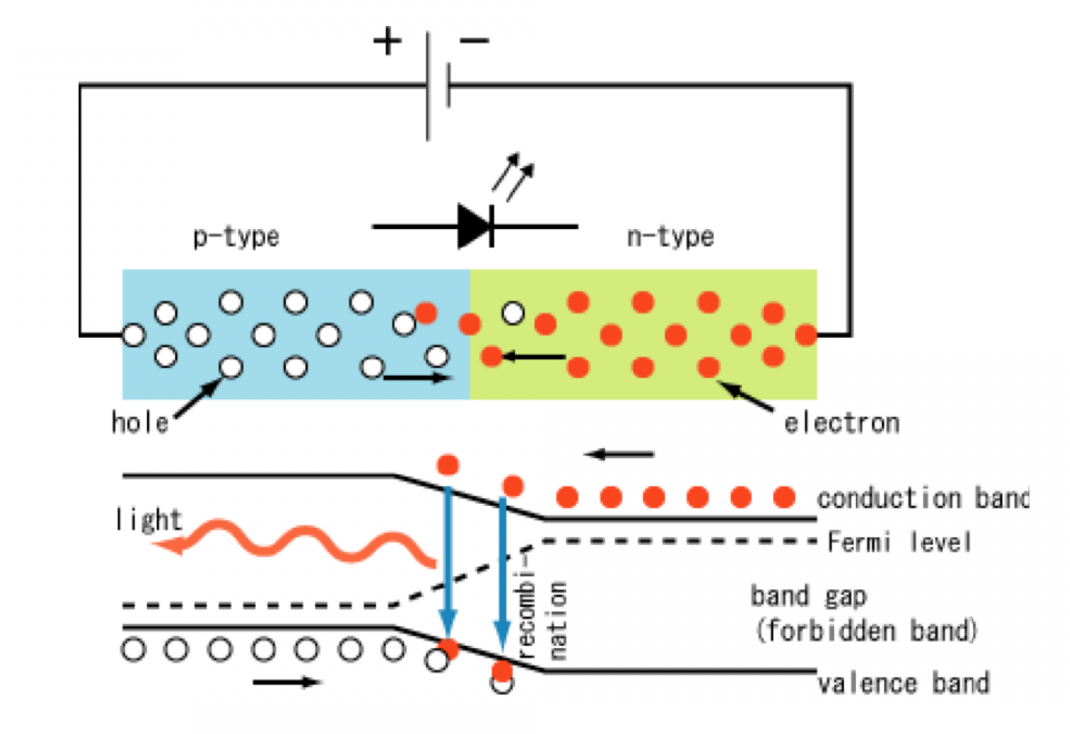
Thus, due to the flow of these charge carriers, recombination occurs, and the recombination indicates that the electrons in the conduction band jump below the valence band. When an electron jumps from one band to another, the electron will emit electromagnetic energy in the form of a photon, which is equal to the forbidden energy range.
Applications of light-emitting diodes
There are many uses for light-emitting diodes, but some of their uses are as follows.
LEDs are widely used as billboards or entertainment backgrounds in LED screens.
LEDs are used in household LED lights.
LED fluids are used as industrial lamps.
Roads are used for street lights and traffic lights.
Used for digital clocks and calculators.
Advantages of LEDs:
1. Temperature range - the working range is in a wide range of 00C-700C
2. Switching time - LED switching time is subject to 1ns. As a result, they are useful in dynamic operations that use a large number of arrays.
3. Low Power Consumption - It uses very little power and can operate even if the given power is low.
4. Better Control - The radiant power of an LED is a function of the current flowing through it. Therefore, the light intensity of the LEDs can be easily controlled.
5. Economical and reliable- LED is cheap and has high reliability.
6. Small size, strong portability - small size, can be stacked together to form an alphanumeric display.
Disadvantages of LEDs:
1. Overvoltage or Overcurrent - When the power exceeds a certain limit, there is a possibility of loss. The same function can be achieved even at lower power.
2. Overheating due to radiated power - heating up with excessive increase in radiated power. This may damage the indicator.


